November 17th, 2019
Have you ever seen an item on Amazon that you wanted, but it was more than you wanted to spend? Did you check the price daily, hoping for a sale? What if I told you you could automate this process with Python? If you answered ‘yes’ or ‘cool’ to any of these questions, then keep reading.
The item I am interested in is the Sony WH1000XM3 Noise Cancelling Headphones. I want some quality noise cancelling headphones, but $348 is more than I want to spend right now. Also, I don’t want have to check the price daily, but I want to know if the price ever drops. Additionally, if the price drops below a certain price, I want to have an email sent to me with the new price and a link to the item on Amazon.
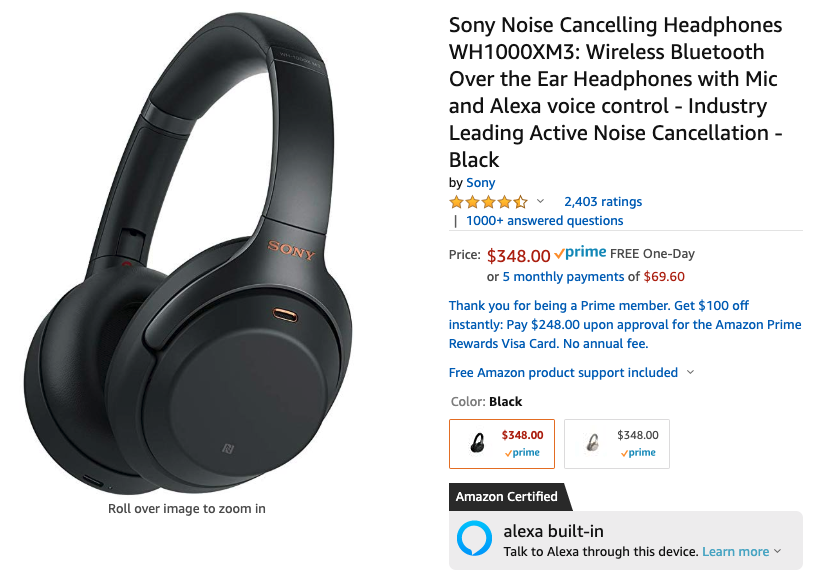
This project idea is based on a video from Dev Ed on Youtube. If you haven’t seen that video, You can check it out here.
Without any more delay, let’s get started.
Setup
To create this program, we need to import 3 libraries to use in our python script. The 3 libraries we need are requests, BeautifulSoup and smtplib.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import smtplib
If you are not familiar with these libraries, requests is used to get the HTTP content from the webpage into our script. BeautifulSoup will help us to search through the html text and pull out specific things we are interested in such as the product name and the price. Smtplib is used to interact with our email server. We will use this to send emails.
For more information, I suggest you check out the documentation of each of these libraries.
Now that all our libraries are imported, next we save the url for the item listing into the variable URL.
URL = 'https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07G4MNFS1/ref=sspa_dk_detail_0?psc=1&pd_rd_i=B07G4MNFS1&pd_rd_w=0tre1&pf_rd_p=45a72588-80f7-4414-9851-786f6c16d42b&pd_rd_wg=uOzSd&pf_rd_r=28TPM13C7R936AHWYJHN&pd_rd_r=6a717b03-9742-43fa-9980-b0adeee91ffc&spLa=ZW5jcnlwdGVkUXVhbGlmaWVyPUExSDdBQ1pOQUZMTlJTJmVuY3J5cHRlZElkPUExMDA4ODA5M1BLRlRBMk01SldINyZlbmNyeXB0ZWRBZElkPUEwNzM1MDE1MkNFWkJORFZBMUpXNCZ3aWRnZXROYW1lPXNwX2RldGFpbCZhY3Rpb249Y2xpY2tSZWRpcmVjdCZkb05vdExvZ0NsaWNrPXRydWU='
Next we get the user agent of our browser and store it in a dictionary called headers with key = “User-Agent” and value as your user agent. Headers is then used in our get request which pulls the imformation from the Amazon web page and brings it into our program.
headers = {
"User-Agent": 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_14_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/78.0.3904.97 Safari/537.36'}
page = requests.get(URL, headers=headers)
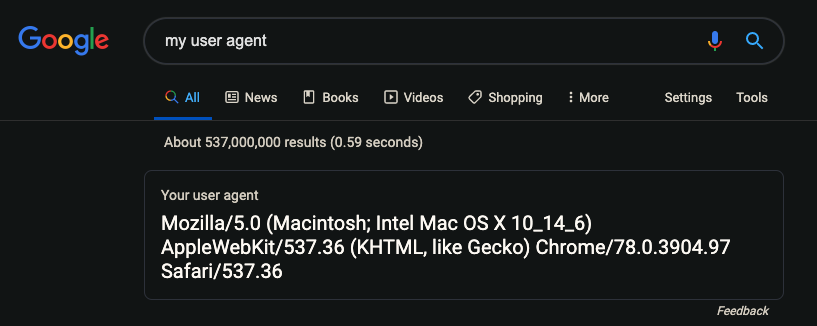
You can get your user agent by searching “My user agent” in Google. Copy and paste it exactly as shown in the search results.
Functions
Our python script will contain 2 functions, check_price() and send_email(). The check price function will get the price from Amazon and check if it is below the desired threshold. If the price is below the desired threshold, it will call the send email function. The send email function will send an email alerting me that the price has dropped.
Here I define check_price():
def check_price():
soup1 = BeautifulSoup(page.content, "html.parser")
soup2 = BeautifulSoup(soup1.prettify(), "html.parser")
product_title = soup2.find(id= "productTitle").get_text().strip()
price = soup2.find(id="priceblock_ourprice").get_text().strip()
converted_price = float(price[1:])
# price check of desired price
if converted_price < 320:
send_email(price = price)
else:
print(f"Price still too high.({price})")
Check_price() first gets the page content using BeautifulSoup. Then it uses the prettify method from BeautifulSoup to clean up the page content and save that as soup2. Using soup2, the function pulls out the product title and price from the webpage using the find() method. Finally, I convert the price from a string to a float.
Now that we have the price, we can compare to the price threshold where we want to be alerted (in my case $320). Using an if statement, we check if the price is below our threshold. If it is, the send_email() function is called with product title and price as parameters. If the price is not below the threshold, the function returns nothing.
Now we define send_email():
def send_email(price):
server = smtplib.SMTP(host = 'smtp.gmail.com', port = 587)
server.ehlo()
server.starttls()
server.ehlo()
# login to email using two-step google verification app password
server.login('adamreynoldsdata@gmail.com', '<password>')
subject = 'Price Drop to ' + str(price) +' on Sony Headphones'
body = 'Check the Amazon link: ' + str(URL)
msg = f"Subject: {subject} \n\n {body}"
server.sendmail(
from_addr = 'adamreynoldsdata@gmail.com',
to_addrs = 'adamreynolds89@gmail.com',
msg = msg
)
print('Email has been sent!')
You’ll notice that send_email() has one parameter, price. This will be used in the email to let me know the new price of the item. First, a server must be established with a host and port. I used a gmail account, and found the host and server in a quick Google search.
If you are not familiar with SMTP, it stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. This is how email servers communicate to send and receive messages. To establish the connection to the server I run server.ehlo(), server.starttls(), server.ehlo(), and server.login(). These commands finalize the connection and I am now ready to send an email.
The subject contains the new price that we brought in as a parameter from check_price(). The body of the email includes the link using the URL variable defined earlier. Finally, to send the email, we call server.sendmail(). This method requires a from address, to address, and a message.
Making the Code Run
To make our program work, we simply need to call check_price(). I do not need to explicitly call send_email() because that is handled inside of check_price(). I added a simple print statment in send_email() to let me know if the email was sent sucessfully or not.
check_price()
Price still too high.($348.00)
Setting Up the Code to Run Automatically
Automating the price checking is great, but it’s still a pain if I have to find and run the program each day to check the price. It would be better if I could set up the script to run once daily automatically. Since I am on Mac, I can use crontab, a built-in unix job scheduler. I could also use a more reliable mac utility called launchd, but crontab is more simple, and since this is not a production job, I’m ok if it fails occaisionally.
Note: if you are on windows, you can use task scheduler. This video does a good job of explaining how to set that up.
You can set up a cron job with the following steps:
- In terminal and type crontab -e. This will open the crontab file for editing.
- Type i to enter insert mode.
- Edit the file to include the schedule and the command you want to execute. For more information on schedule format check out crontabguru.
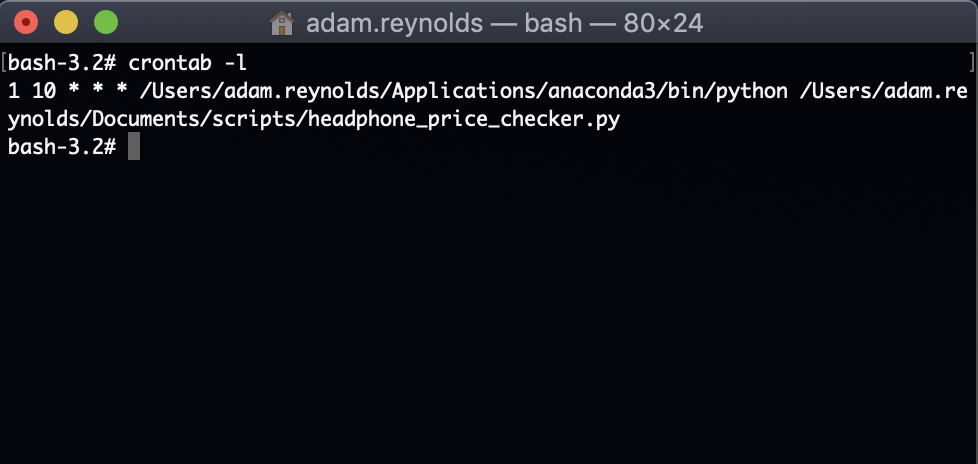
- Since I want to run my command daily at 10 I enter the following for schedule
0 10 * * *. - The command is
/Users/adam.reynolds/Applications/anaconda3/bin/python /Users/adam.reynolds/Documents/scripts/headphone_price_checker.py - The command consists of my python location and the location of my python script.
- Once you have added the information into your crontab file type esc to escape edit mode, then :w to save (write) the changes and :q to quit crontab editing. This will take you back to the main terminal.
- To view the crontab saved correctly type crontab -l in the terminal to view the job. It should look something like this:
- Since I want to run my command daily at 10 I enter the following for schedule
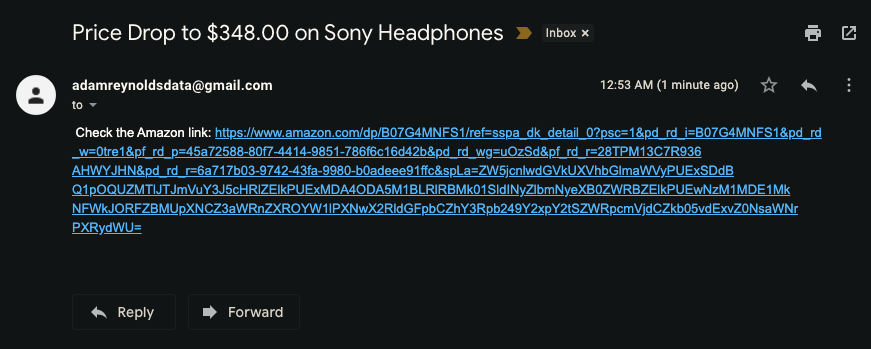
I temporarily adjusted the threshold to test the email sending process. When I check my email, I see the following:

The body of the email looks like this:
And finally, when I click the link, it takes me here:

So, there you have it. An automated Amazon price checker. Shoot me a message if you have any questions or suggestions for future projects.
